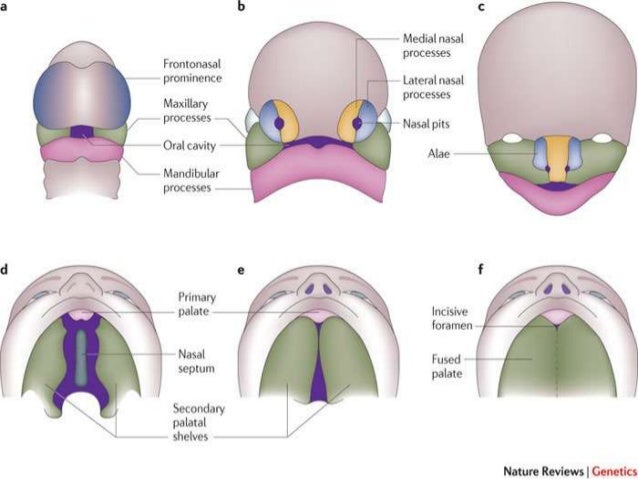
Face
5 processes formed by proliferation of neural crest cells (ectoderm)
These cells migrate from mesencephalon and rhombencephalon into arches
- 1 frontonasal process – cranial to stomodeum
- 2 maxillary processes – lateral, from 1st pharyngeal arch
- 2 mandibular processes – caudal, from 1st pharyngeal arch
1 frontonasal process:
- 2 nasal placodes develop
- Each invaginated to form:
- Nasal pit – forms nasal cavities – open in pharynx posteriorly
- Lateral nasal fold – ala of nose
- Medial nasal fold – fuse together to form:
- Surface: middle part of nose, filtrum of upper lip
- Deep: anterior upper jaw with Incisor teeth, primary palate with incisive fossa
NB: Also forms nasal septum
2 maxillary processes:
- Grow medially
- Fuse with medial nasal fold – form upper lip
- Fuse with lateral nasal fold – form nasolacrimal duct
- Fuse with mandibular process – forms cheeks
- Forms palatine shelves
2 mandibular processes:
- Fuse with each other medially – form lower lip and chin
- fuse with maxillary process – forms cheeks
NB: Degree of fusion of max. and mand. processes determine width of mouth
Palate
Origin: Neural crest cells (ectoderm)
- Formed by primary and secondary palate
- Primary palate formed from frontonasal process (fusion of medial nasal folds)
- Secondary palate formed from 2 palatine shelves, which arise from maxillary process
- 2 palatine shelves fuse with each other medially, and primary palate anteriorly
- Nasal septum descends downwards and fuses with palate in midline
- Anterior part of palate ossifies and posterior part remains fleshy to form hard and soft palate
Anomalies of face and palate:
- Inclusion dermoid – cystic swellings around lines of fusion of face
- Macrostomia – large mouth, incomplete fusion between max. and mand. processes
- Microstomia – small mouth, excessive fusion between max. and mand. processes
- Oblique facial cleft – failure of fusion between maxillary and frontonasal process
- Lateral cleft upper lip – unilateral or bilateral
- Cleft palate – unilateral, bilateral, only soft palate or cleft uvula