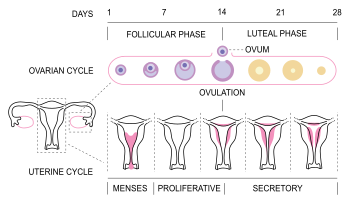
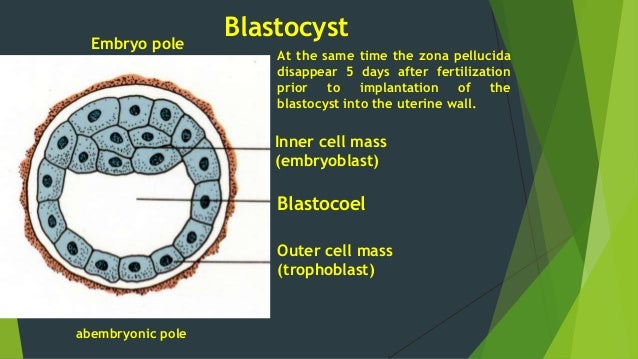
Also known as the week of two’s:
1. Two embryoblast layers form:
- Endoderm (Hypoblast)
- Ectoderm (Epiblast)
Therefore forming a bilaminar germ disc
2. Two trophoblast layers form:
- Cytotrophoblast
- Syncytiotrophoblast – has lacunae
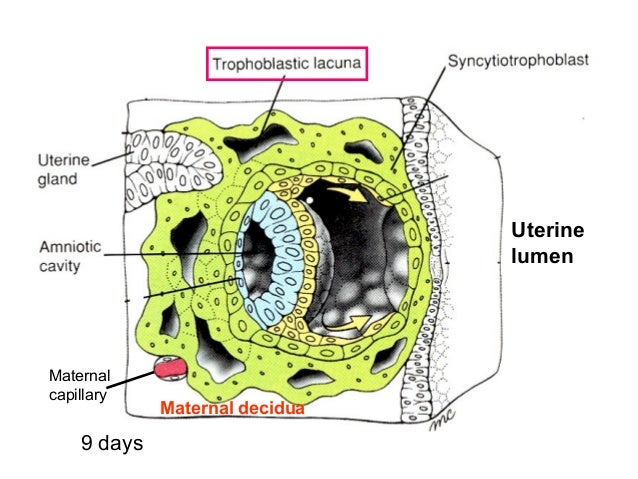
3. Two cavities form:
- Amniotic cavity – the cytotrophoblast cells surrounding the amniotic cavity become amnioblast cells
- Primary yolk sac – endodermal cells grow down, line cytotrophoblast forming Heuser’s membrane (exocoelomic membrane)
Heuser’s membrane/exocoelomic membrane – Short lived combination of hypoblast cells and extracellular matrix
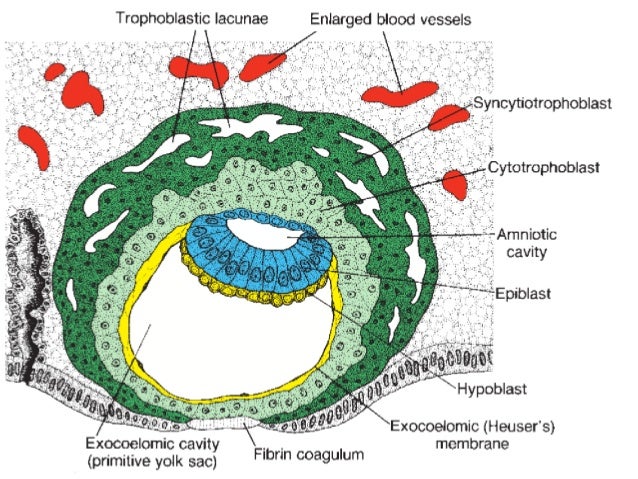
4. Two extraembryonic mesodermal layers form:
In the cytotrophoblast, extraembryonic mesoderm forms, in which lacunae appear and fuse to form extraembryonic coelom. Therefore dividing the extraembryonic mesoderm into 2 layers.
- Somatopleuric mesoderm – lines cytotrophoblast and amniotic cavity
- Splanchnopleuric mesoderm – lines primary yolk sac

NB:
- Secondary yolk sac also forms, when a large part of primary yolk sac separates and disappears leaving the smaller part. It is completely lined with endoderm.
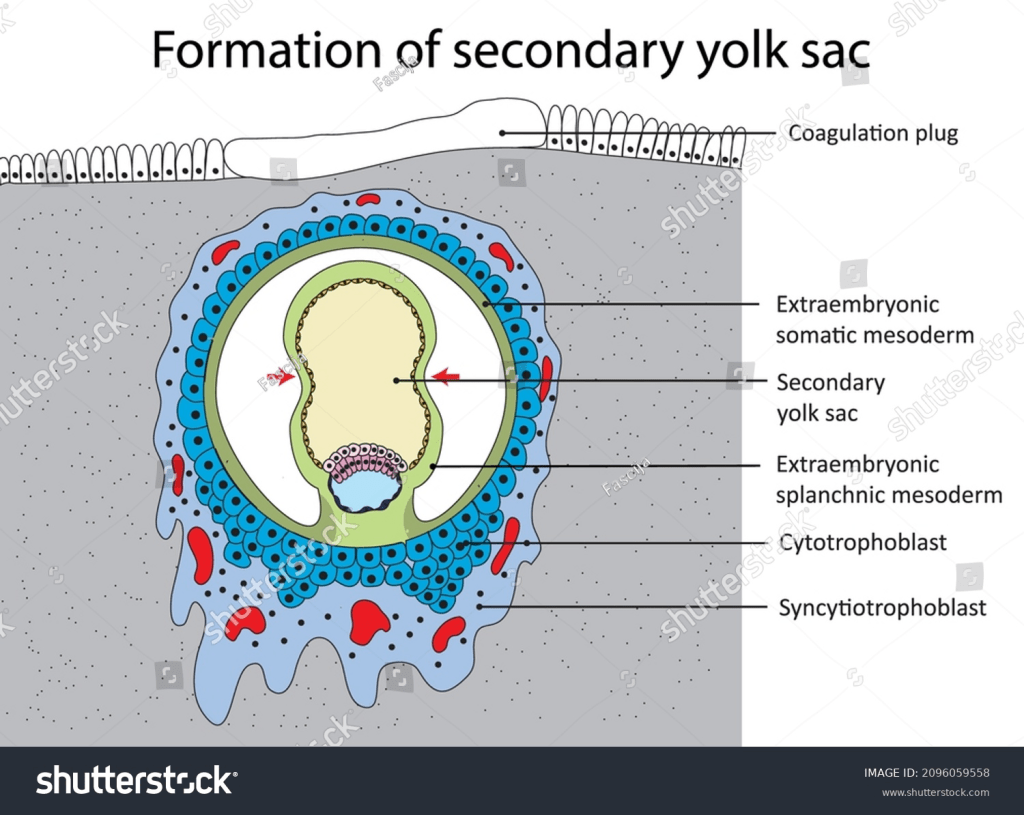
- Primary chorionic villi forms – cytotrophoblast projects into syncytiotrophoblast (more in the next chapter)
Syncytiotrophoblast – Placental barrier between maternal and fetal blood